Knee Gout Symptoms: Understanding and Managing the Painful Condition
Knee gout, also known as gouty arthritis, is a form of arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, leading to inflammation and severe pain. It typically affects the big toe, but it can also manifest in other joints such as the knees. Understanding the symptoms and effectively managing this painful condition is crucial for maintaining a good quality of life for those affected.
Understanding the Causes of Knee Gout
Knee gout occurs when urate crystals accumulate in the knee joint, leading to inflammation, swelling, and intense pain. Gout itself is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia. Here are some common causes of knee gout:
- Dietary Factors: Consuming foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, shellfish, and certain types of fish, can contribute to elevated uric acid levels. Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption, particularly beer and spirits, can increase the risk of gout attacks.
- Genetics: Some people are genetically predisposed to produce higher levels of uric acid or have reduced excretion of uric acid through the kidneys, increasing their susceptibility to gout.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese is associated with higher levels of uric acid in the blood and an increased risk of developing gout. Excess weight puts additional stress on the joints, including the knees, which can exacerbate symptoms.
- Dehydration: Inadequate hydration can lead to higher concentrations of uric acid in the blood and a greater likelihood of urate crystal formation. Staying well-hydrated is important for flushing out uric acid and reducing the risk of gout.
- Joint Trauma or Injury: Previous trauma or injury to the knee joint can predispose it to gout attacks. Damage to the joint can disrupt normal function and increase inflammation, making it more susceptible to urate crystal deposition.
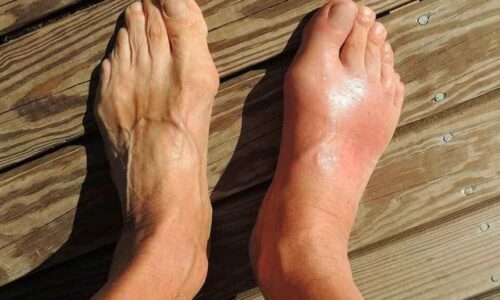
Recognizing the Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of knee gout is essential for early diagnosis and timely treatment. Some common symptoms include:
- Intense Knee Pain: The pain in the affected knee can be excruciating and sudden, often waking the person from sleep.
- Swelling and Redness: The knee joint may become swollen, warm, and tender, with the skin appearing red and inflamed.
- Limited Range of Motion: Due to inflammation, it may become challenging to bend or move the knee fully.
- Fever: In some cases, individuals may experience a low-grade fever accompanying the gout flare-up.
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment
Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective management. If you experience symptoms of knee gout, consult a healthcare professional who may:
- Perform a Physical Examination: The doctor will examine the affected knee for signs of inflammation and tenderness.
- Order Blood Tests: Blood tests can measure the levels of uric acid in the bloodstream.
- Aspiration of Joint Fluid: A sample of fluid from the affected knee may be taken and analyzed for the presence of uric acid crystals.
Managing Knee Gout
While knee gout can be painful, there are several ways to manage the condition and reduce its impact on daily life:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and colchicine can help relieve gout pain and inflammation.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and weight management can prevent gout attacks.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated helps flush excess uric acid from the body.
- Rest: During a gout flare-up, rest the affected knee to avoid further irritation.
- Ice: Applying ice packs to the knee can help reduce swelling and ease pain.
Preventing Knee Gout Flare-ups
Preventing knee gout flare-ups is of paramount importance for those who suffer from this painful condition. By adopting certain lifestyle changes and following a gout-friendly regimen, individuals can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of gout attacks. Below are some key strategies to prevent knee gout flare-ups:
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is critical in the treatment of gout. Drinking enough of water stimulates the removal of uric acid through urine and helps to maintain a healthy equilibrium of uric acid in the body. This lowers the concentration of urate crystals in the joints, reducing the likelihood of gout flare-ups. Drink at least 8 to 10 glasses of water every day.
- Limit Alcohol and Purine-rich Foods: Alcohol consumption, especially beer, is associated with an increased risk of gout attacks. Beer is rich in purines, which contribute to elevated uric acid levels. Additionally, due to their purine concentration, some meals such as red meat, organ meats, shellfish, and high-fructose corn syrup can cause gout flare-ups. Modifying your consumption of these products can help you manage your gout more efficiently.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Overweight or obesity is a major risk factor for knee gout. Excess body weight puts additional strain on the joints, increasing uric acid production and increasing the incidence of gout episodes. Individuals can acquire and maintain a healthy weight by eating a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical exercise, lowering the strain on their knees and the likelihood of gout flare-ups.
- Regular Exercise: Regular exercise is good for general joint health and can help avoid flare-ups of knee gout. Swimming, cycling, and walking are low-impact exercises that are easy on the joints while giving significant health advantages. Exercise also helps with weight control and improves circulation, both of which help to reduce the incidence of gout episodes.
In conclusion, knee gout is a painful ailment that can have a substantial influence on one’s quality of life. Individuals may get control of their knee gout and improve their joint health by recognizing the symptoms, understanding the reasons, and implementing effective preventative actions.